What is Thermal Leakage and How to Reduce Its Risks
What is Thermal Leakage?
Thermal runaway is an uncontrolled reaction that can occur in lithium ion batteries. Damage to the battery or a short circuit may cause heat and pressure to build up in the battery. If this reaches to a certain level, it triggers chemical reactions that generate more heat and pressure, causing a positive feedback loop. Thermal leakage can spread rapidly from one battery to another, causing catastrophic explosions and fires. Thermal leakage by-products may contain large amounts of flammable hydrogen and other toxic fluoroorganic gases.
Potential triggers of thermal leakage include damage such as overcharging of the battery, overheating of the battery or exposure to high temperatures, excessively high discharge rate, short circuit or puncture. Any of these factors can destabilize the high-energy materials and organic components of the battery, causing them to generate their own heat. If this heat does not dissipate quickly enough, the battery temperature will continue to increase, which will speed up the heat release process.

How to Reduce Thermal Leakage?
Some of the preventive safety measures include a robust battery case, an efficient cooling system, and protective design and control features. Flame retardant additives can be used in the electrolyte or separator to improve the thermal stability of the battery and prevent it from igniting in the first place.

Prevention Zone
Stage 1: Battery Abuse
At this initial stage, thermal, electrical or mechanical abuse causes cell damage, causing battery cell temperatures and pressures to increase.
Stage 2: Non-Gas Production
As cell temperatures and pressures rise, flammable gases escape from the cells. This is the critical point at which action should be taken to prevent thermal leakage and fire incident.
Stage 3: Thermal Leakage
Thermal leakage indicates the end of the prevention zone and the beginning of the containment zone. Temperatures rise rapidly and smoke forms. At this point, a catastrophic failure is imminent.
Enclosure Zone
Stage 4: Fire Formation
After thermal escape, fever occurs. Lithium-ion battery racks are configured to maximize energy storage density, while this also allows for rapid fire spread. When a fire occurs, the flame can easily pass into adjacent cells and building materials and become uncontrollable.

Blog Posts

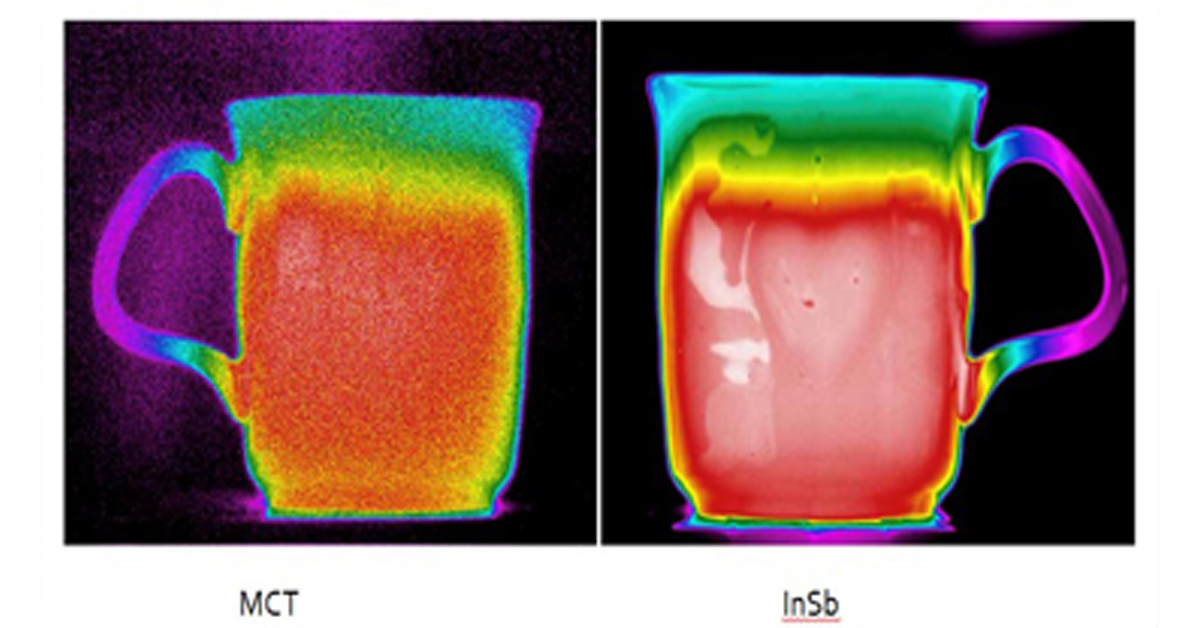
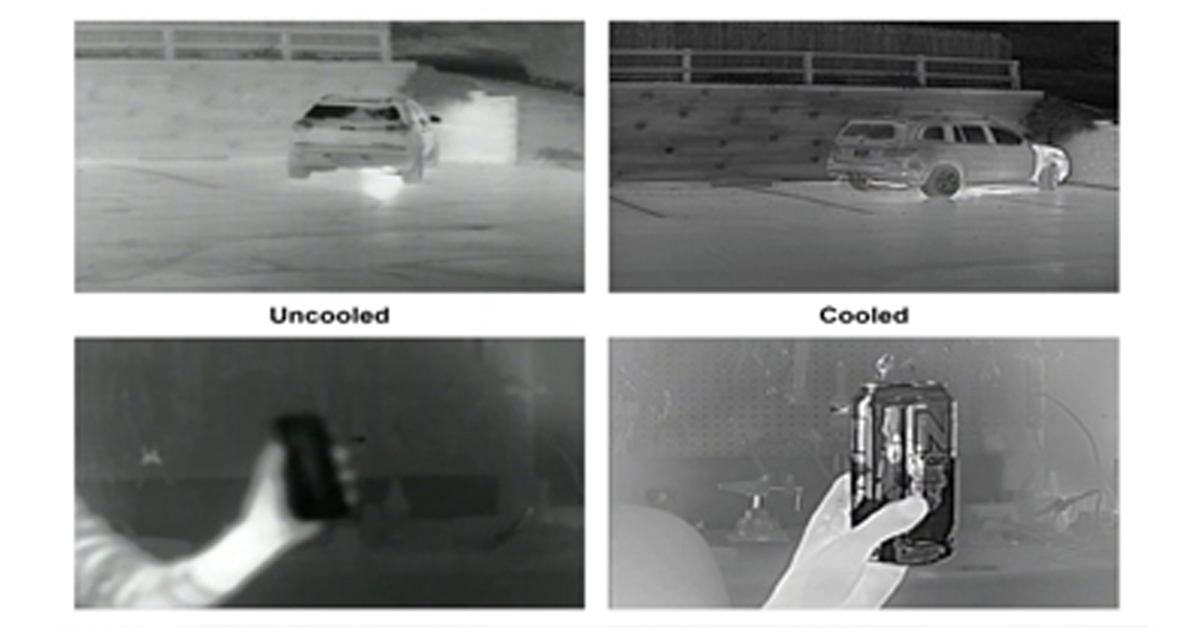
Thermal Camera Selection
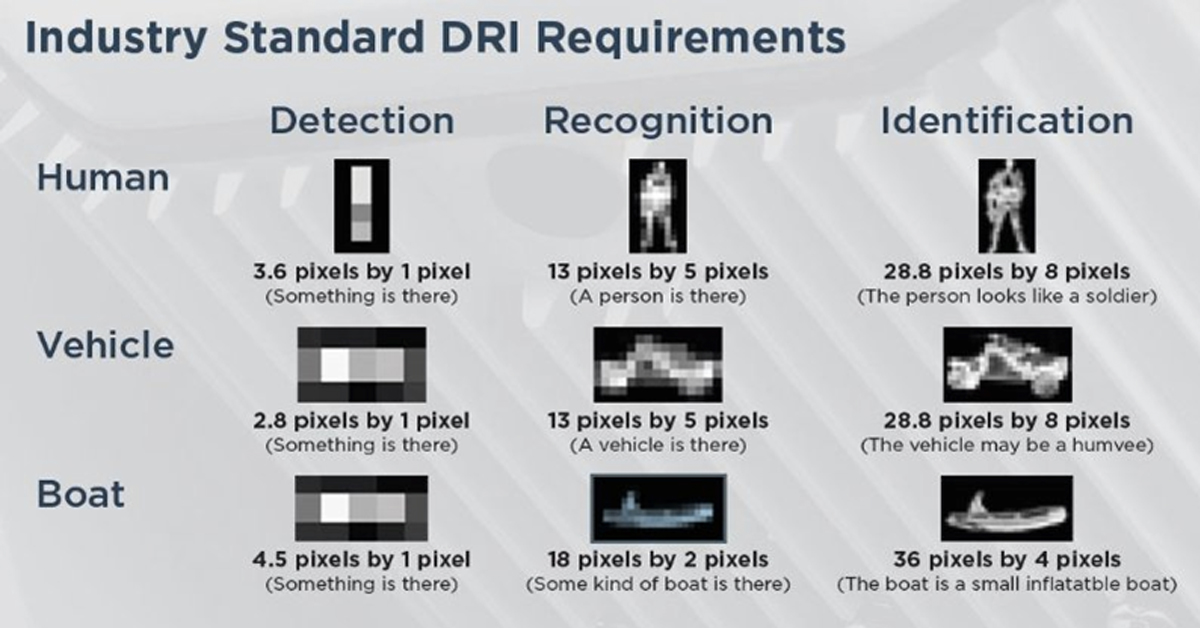
How Far Can I See?
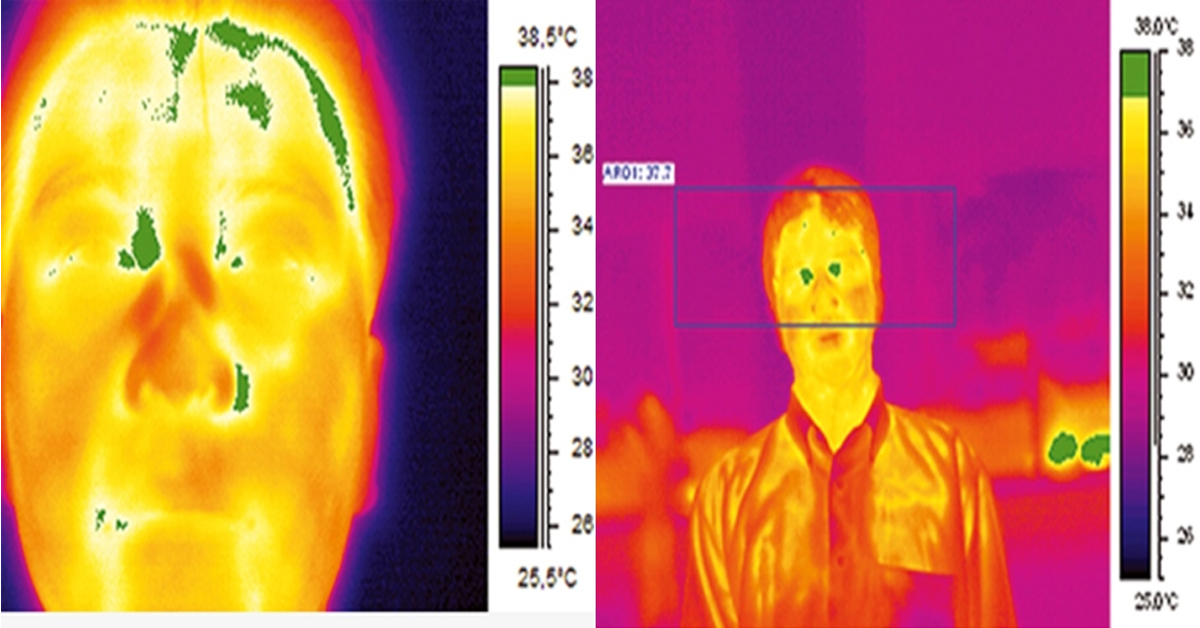
How Should Human Temperature Be Measured?
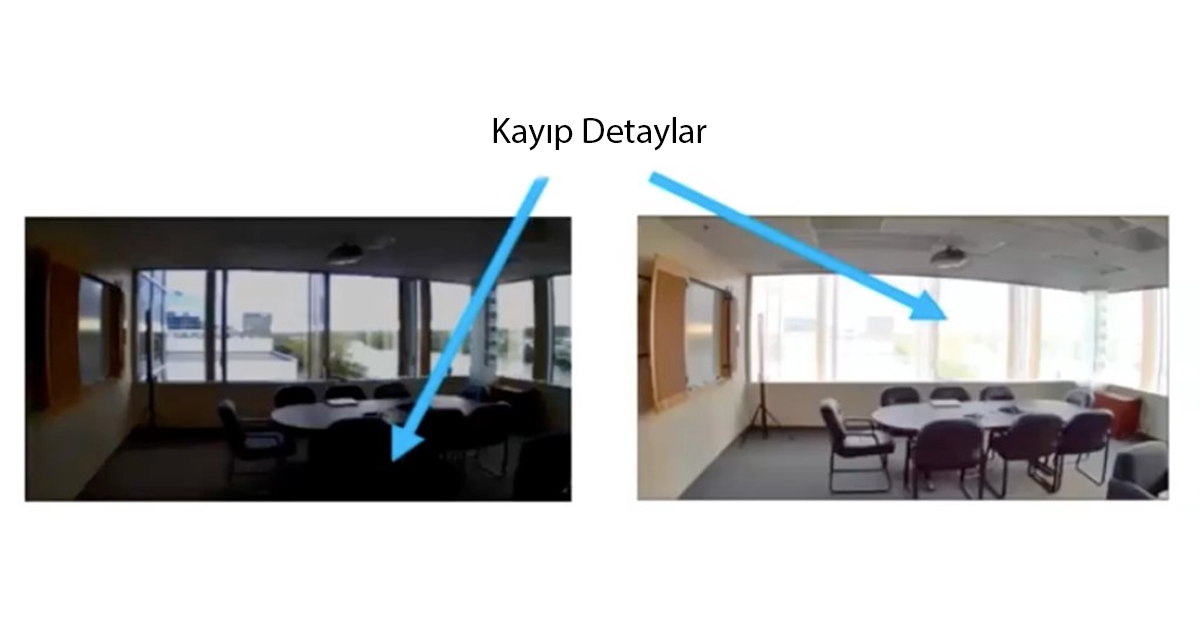

What is Wide Dynamic Range?

MYNOISE AUDIO MIXER REVIEW

WHAT IS A WIRELESS DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM?

POE VS. POE+ VS. POE++: CHOOSING THE RIGHT INDUSTRIAL ETHERNET SWITCH FOR YOU

INDUSTRY-LEADING INDUSTRIAL ETHERNET SWITCHES
UNDERSTANDING WHAT THE INDUSTRIAL INTERNET OF THINGS IS
THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN A HUB, SWITCH, & ROUTER

5 Benefits of Thermal Imaging Cameras

DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INDUSTRIAL ETHERNET AND REGULAR ETHERNET

INDUSTRIAL NETWORKING EQUIPMENT USED FOR AUTONOMOUS VEHICLES

CYBERSECURITY: PROTECTING INDUSTRIAL CONTROL SYSTEMS

HOW INDUSTRIAL NETWORKING CAN PROVIDE SECURITY FROM DRONES
.webp)
Thermal Cameras Reveal How to Keep Your Home Cool During a Heat Wave

FLıR ONE PRO
.png)
Unmatched Maritime Awareness with Cooled Thermal Imaging
.png)
What Is the Right Handheld Thermal Camera for You?
.png)
Camera Resolution and Range
.png)
Special Applications for Marine Cameras
.png)
What’s The Difference between Thermal Imaging and Night Vision?
.png)
Can Thermal Imaging See Through Fog and Rain?

Which Cx-Series Camera Is Right for You?
.png)
What is MSX®?

Five Reasons Maritime First Responders Need Thermal Imaging
.png)
3 Distinguishing Features of Superior Thermal Cameras
.png)
Determine Which Visible and Thermal Security Cameras You Need

Bullet vs. PTZ vs. Dome: Which Security Camera Is Right for You?
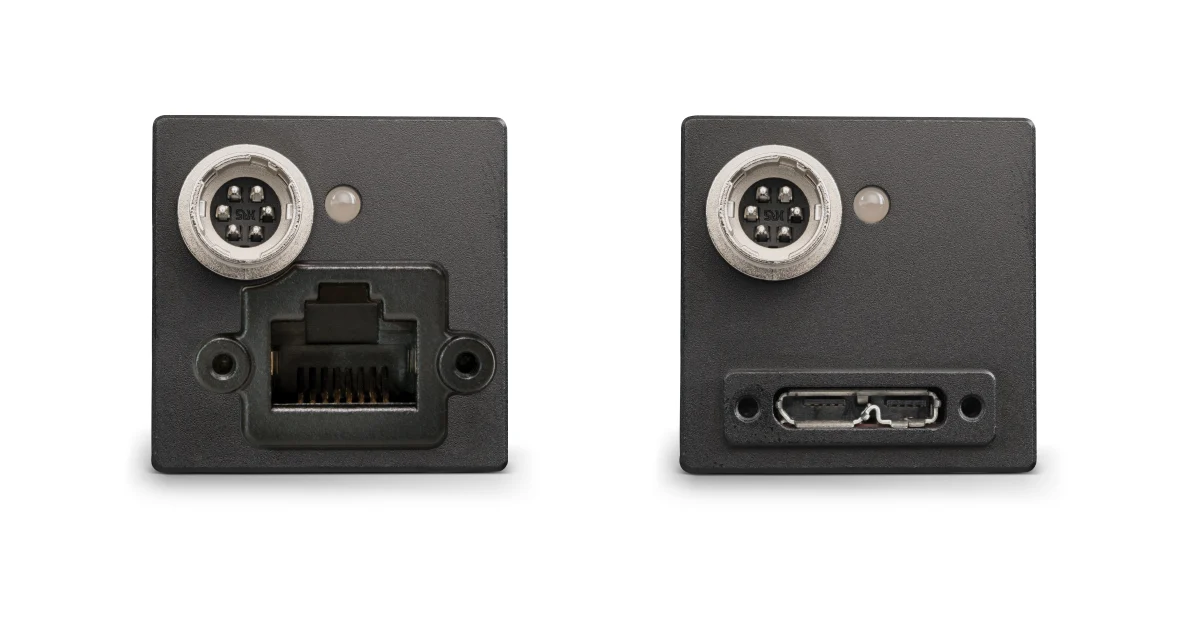
Interfaces for Machine Vision
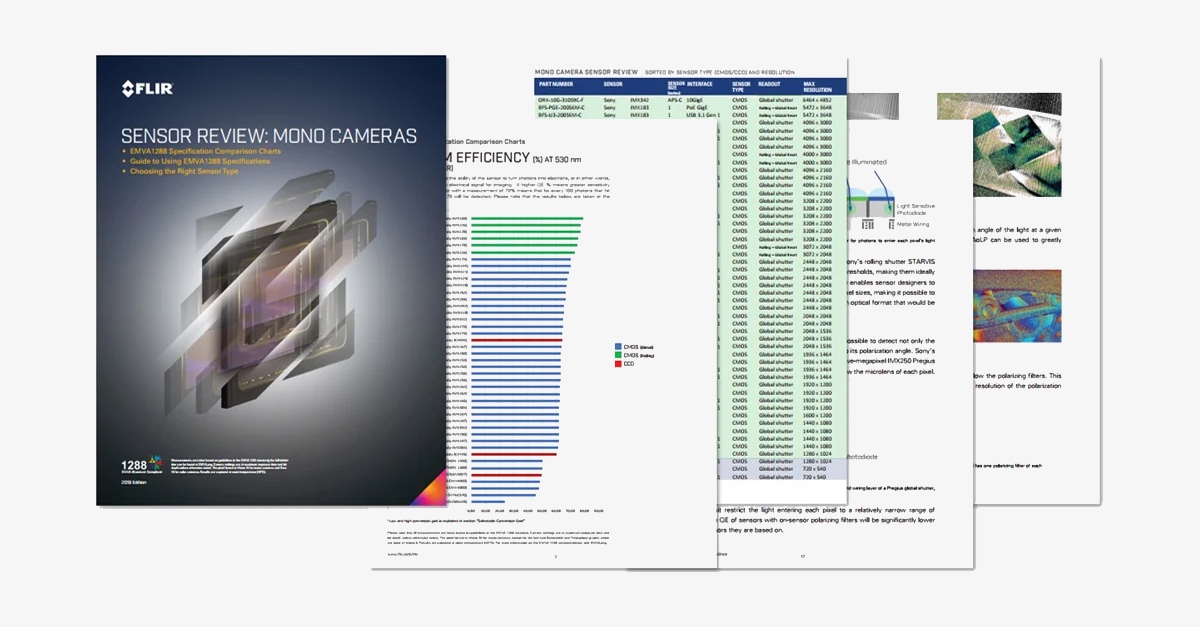
Machine Vision Sensor Review
.png)
Teledyne FLIR, the Industry Leader, Launches Boson +, a Long-Wave Infrared Thermal Imager Module with an Accuracy of Less Than 20 mK
.png)
Whitepaper: IP-Based Security Convergence
.png)
3 Technologies Transforming Safe Cities into Smart Cities
.png)
Insights from the Field: Ensuring Workplace Safety Using Thermal Camera Screening for Entry Control

Thermal Night Vision as a Force Multiplier

Can Thermal Imaging See Through Walls? And Other Common Questions
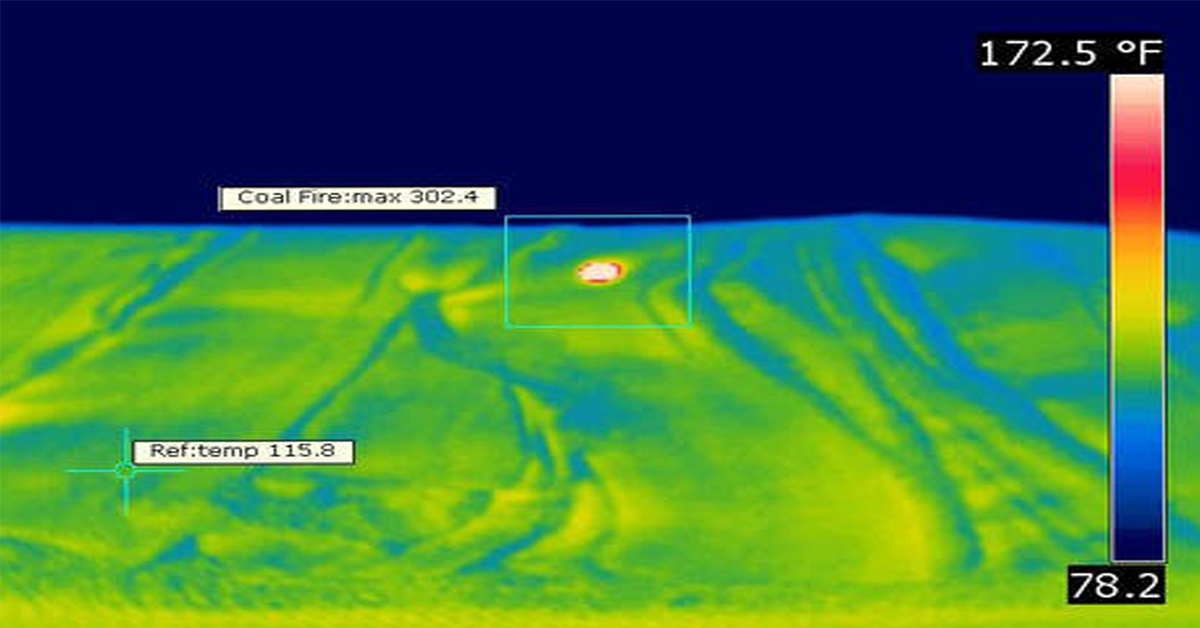
Application Spotlight: Early Fire Detection for Rapid Heat Generation

Protect Personnel and Equipment by Detecting Early Signs of Fire

Teledyne FLIR Launches A500f/A700f Cameras for Fire Detection and Condition Monitoring

Thermal Imaging Cameras Help Guarantee Fire Safety in Tunnels

Thermal Imaging Cameras Help to Prevent Fires

ITS-Series Dual AID Surpasses Standards for Fire Detection Systems in Japan

How Layering Multispectral PTZ Cameras and Radars Improve Perimeter Protection
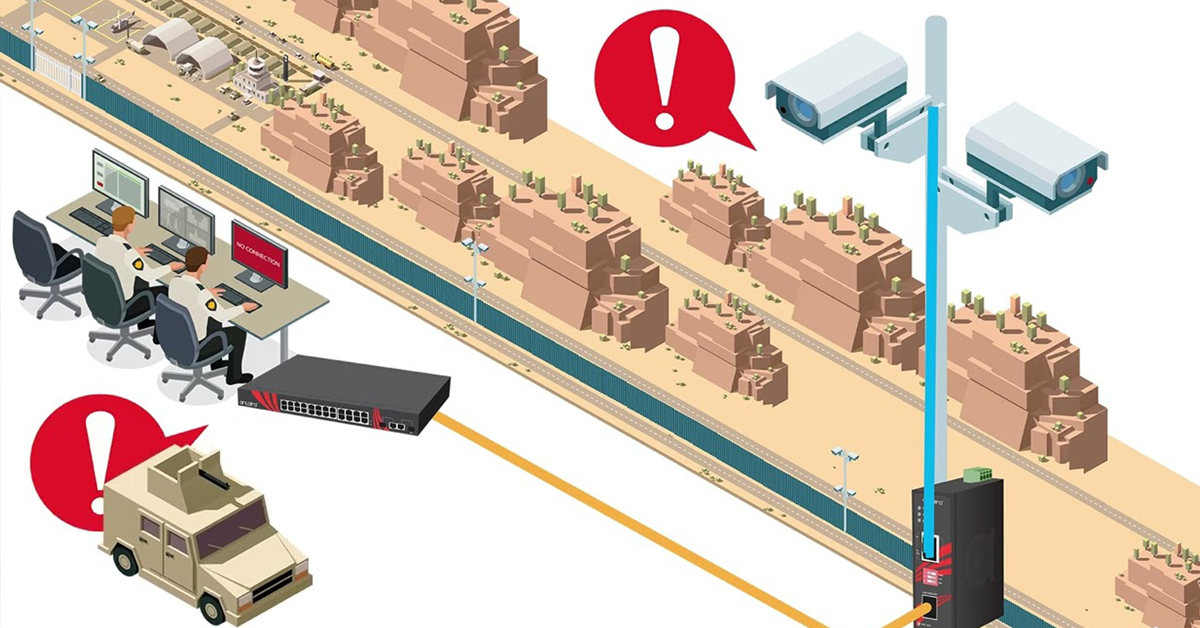
POWER REMOTE RESET TECHNOLOGY - PRRT

Why Yacht Owners are Adding Thermal Imaging Cameras to Minimise the Risk of Lithium-Ion Battery Fires?
.png)
Intelligent Transportation Systems

Best Practices Guide for Perimeter Security Applications

Protect Pedestrians, Bicyclists and More with Thermal Smart Sensors

White Paper: Application of Ground-Based Security Radar to Perimeter Systems

What is Thermal Leakage and How to Reduce Its Risks

Battery Inspection Using Advanced Thermography

Providing ire Protection for Lithium Battery Storage
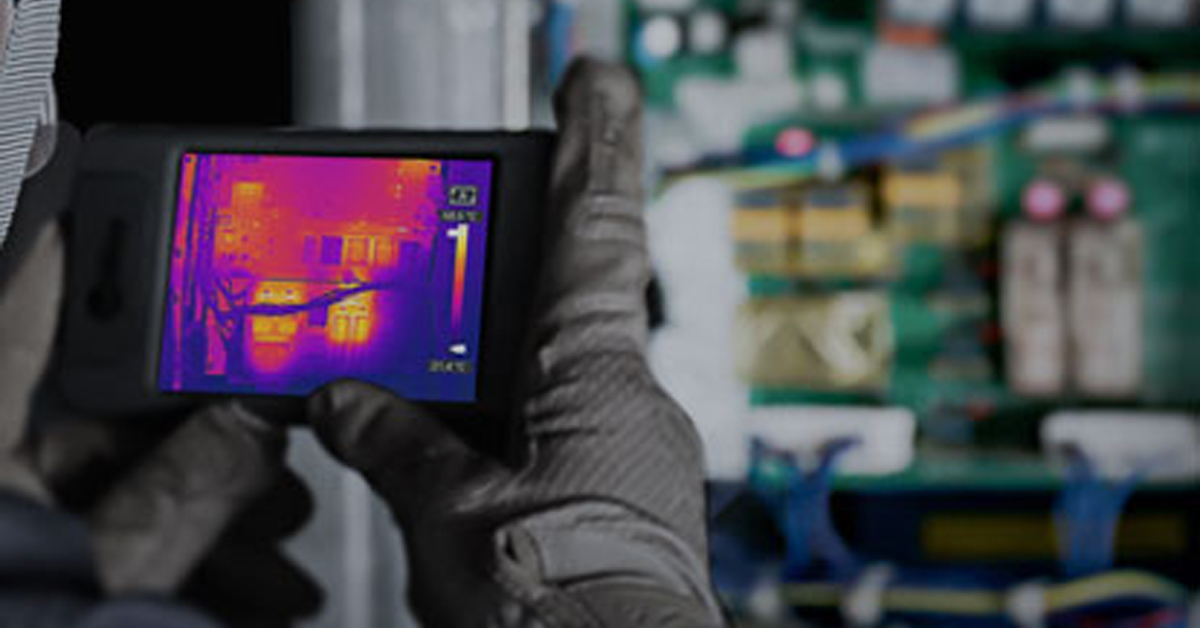

The Power of Thermal Imaging
.png)
Why Panel PCs Are Perfect For Industrial Applications?

Teledyne DALSA
.png)
Advantages of Virtual Barrier Video Analytics for Perimeter Security Systems
.png)
.png)
NASA Takes the Teledyne FLIR Boson Thermal Camera Module Out of this World
.png)
Port Security Enhancement: DP World Yarımca's Trust in FLIR Security Solutions for Effective and Safe Port Operations
.png)
The Importance of Thermal Sensitivity (NETD) for Detection Accuracy
.png)
Bosphorus Boat Show 2025: The Meeting Point of the Maritime World
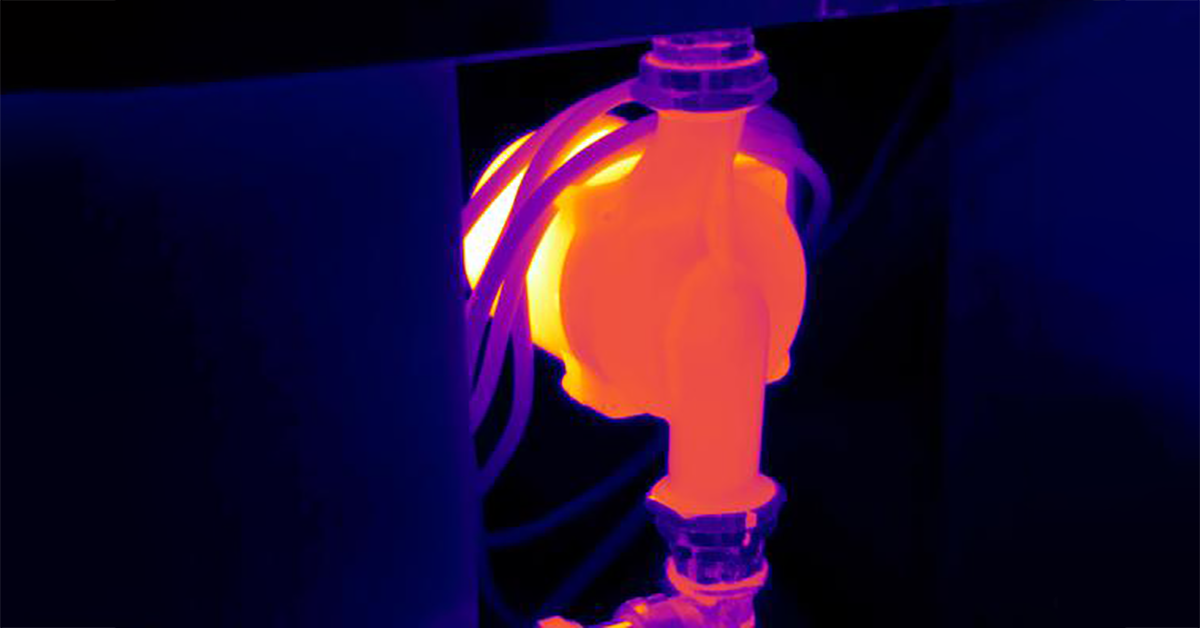

Application Spotlight: Critical Asset Monitoring for Thermal Conditions
.png)
Thermal Imaging for Marine Firefighting
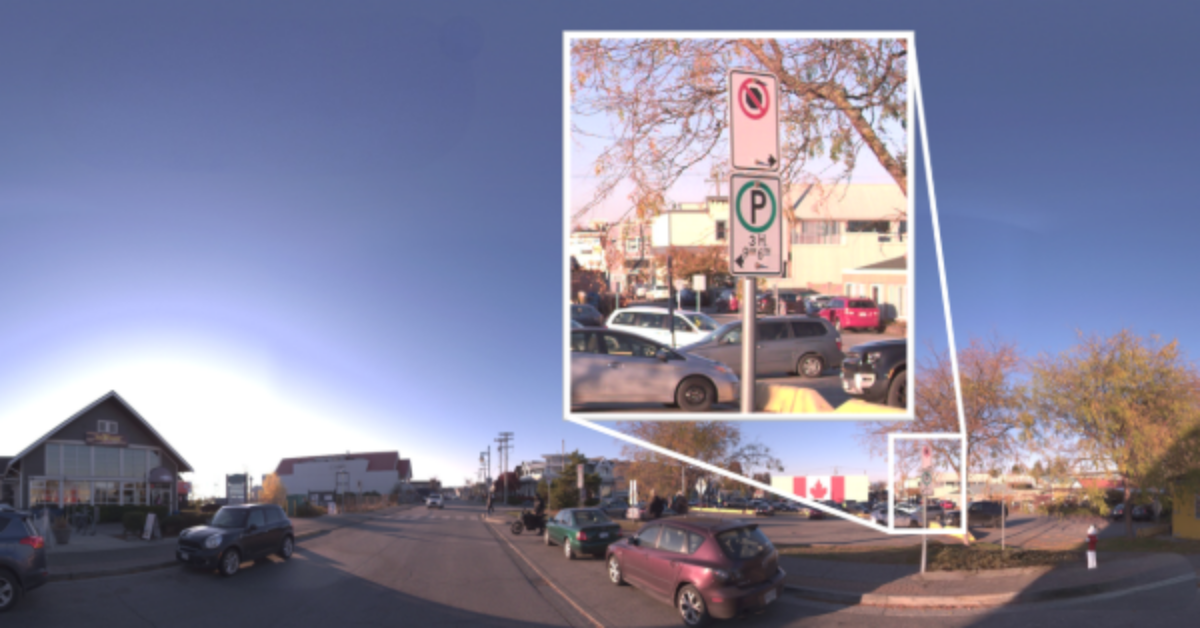

Imaging in Mobile Mapping
.png)
Using Thermal Imaging for Oil Spill Detection

Five Reasons Maritime First Responders Need Thermal Imaging

Case Study: Tackling Compressed Air Leaks in Automotive Parts Manufacturing with Acoustic Imaging

Thermal Night Vision as a Force Multiplier
.png)
Line Scan Contact Image Sensor - AxCIS

Beyond Resolution: What Really Makes a Camera System Work for Mobile Mapping
.png)
Multispectral Marine Cameras for USV Applications
.png)
Stabilizing FLIR Cameras for Smooth Viewing in Rough Waters
 (1).png)