THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN A HUB, SWITCH, & ROUTER
Introduction
Hubs, switches, and routers are all common types of devices to help connect a network. Because they are often integrated into a single device, it can be challenging to understand the distinction between these items. In some cases, the terms may even be used interchangeably, though this is incorrect. The functions and uses of these devices are all very different from one another. Below, we provide a simple guide on the difference between a hub, switch, and router to help you better understand their dissimilarity.
Hub
A hub is a type of device that’s commonly used as a connection point for various devices in a Local Area Network (LAN). It works by receiving packets that arrive at one of its multiple ports, copying the packets, and sending them to its other ports so that all LAN segments can see the data.
When a single port in the hub responds, all other ports will also receive the response. The hub does not have any capability to distinguish which port it should send a data packet to. As such, all connected devices will receive the response and must determine whether they should accept it or not.
In comparison to routers and switches, a hub is the least complex and least expensive device. While they have often been used as a quick and easy way to connect a small network, they are becoming increasingly replaced by switches.
Switch
A networking switch is a type of hardware that uses packet switching to receive and forward data to its intended destination within a network. Essentially, a switch is a more efficient, more intelligent version of a hub.
Perhaps the biggest difference between a hub and a switch is the way that it delivers data packets. Rather than blindly passing along data to all devices in a network, a switch records the addresses of the connected devices. In doing so, it learns which devices are connected to which ports. Then, when a port receives a data packet, the switch reads its destination address and sends it directly to the intended device in the network instead of every single port. As a result, a switch can greatly improve the speed of networks that receive a lot of traffic.
Router
A router is the most intelligent and complex of the three network connection devices listed in this article. Rather than just forwarding data packets to other devices in a single network, routers are designed to forward data packets between two or more networks, as well as direct traffic between them. They are typically located at gateways and can be programmed to understand, direct, and manipulate network traffic.
Many modern routers are designed to integrate the capabilities of a switch and hub router all in a single device. Depending on the application, routers range in size from small broadband devices to large industrial wireless routers.
Blog Posts

Thermal Camera Selection
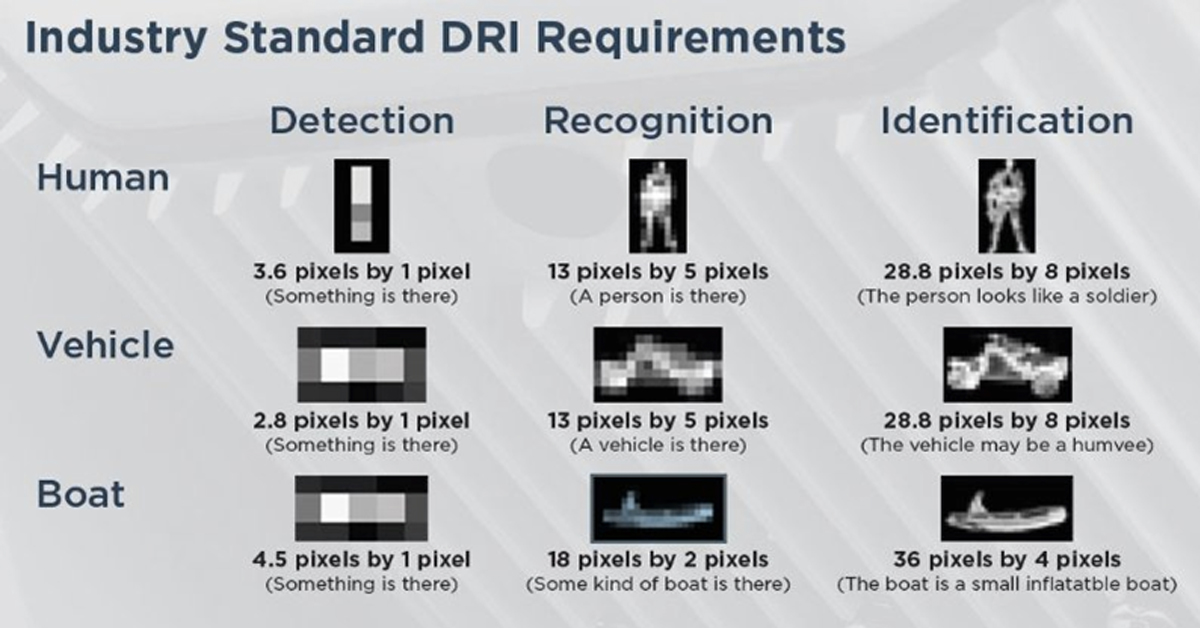
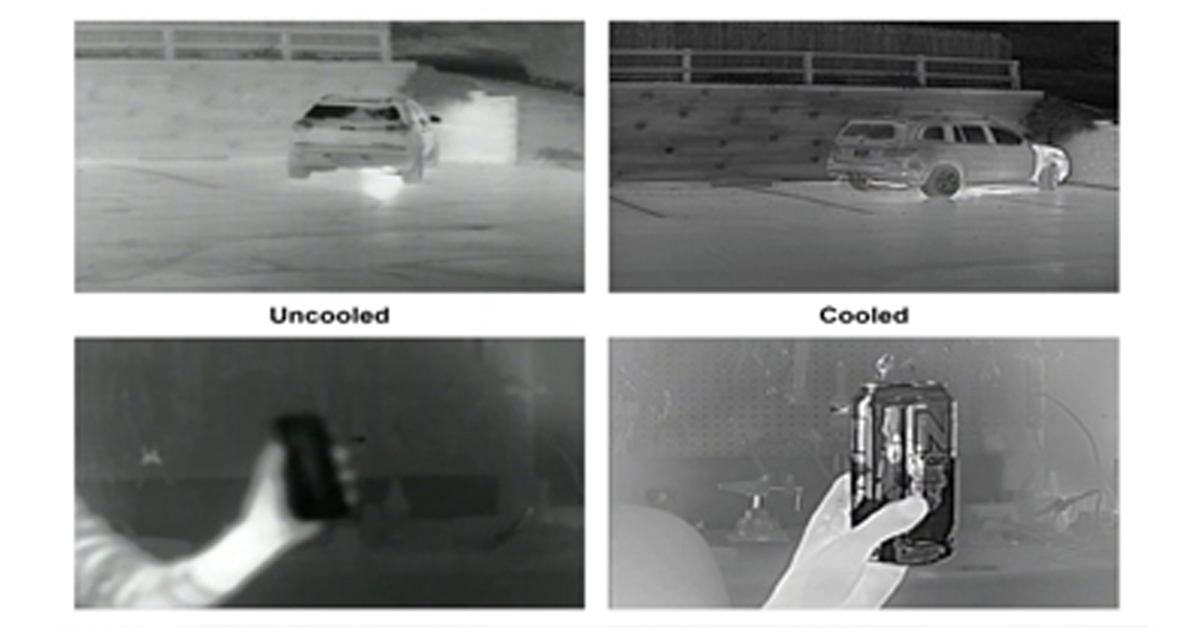
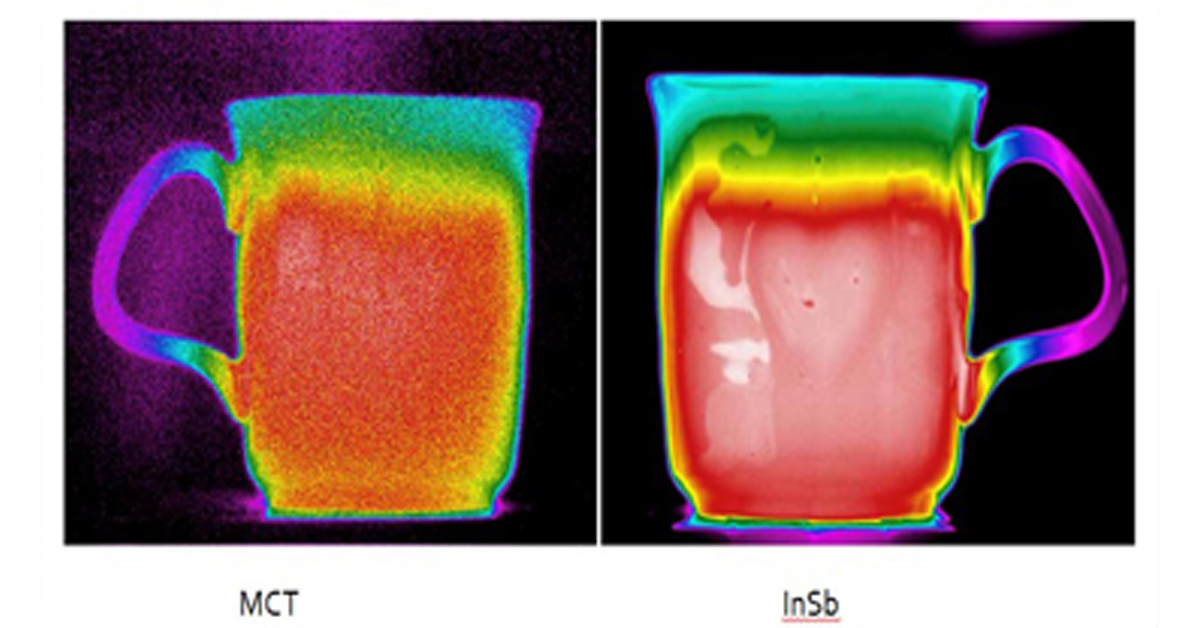
How Far Can I See?
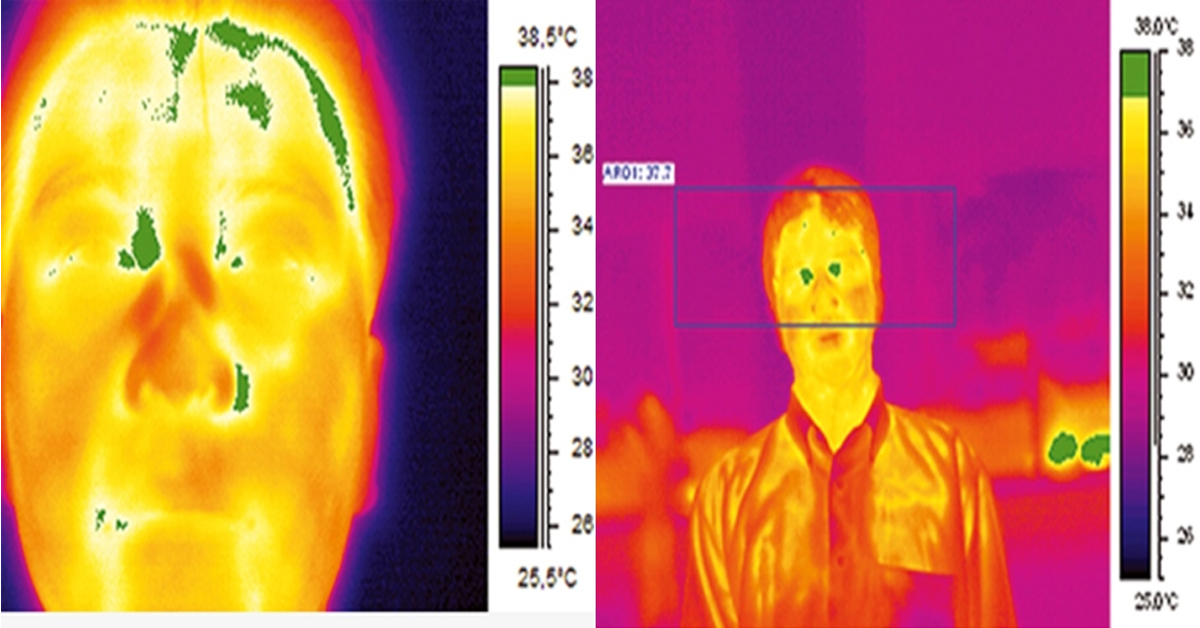
How Should Human Temperature Be Measured?
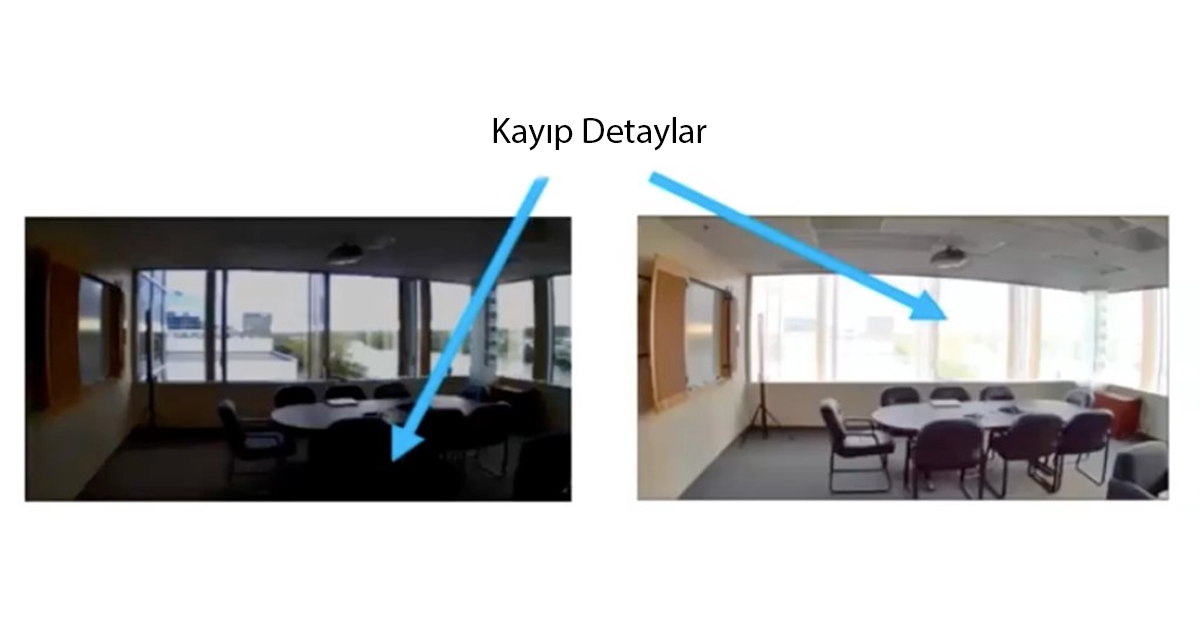

What is Wide Dynamic Range?

MYNOISE AUDIO MIXER REVIEW

WHAT IS A WIRELESS DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM?

POE VS. POE+ VS. POE++: CHOOSING THE RIGHT INDUSTRIAL ETHERNET SWITCH FOR YOU

INDUSTRY-LEADING INDUSTRIAL ETHERNET SWITCHES
UNDERSTANDING WHAT THE INDUSTRIAL INTERNET OF THINGS IS
THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN A HUB, SWITCH, & ROUTER

5 Benefits of Thermal Imaging Cameras

DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INDUSTRIAL ETHERNET AND REGULAR ETHERNET

INDUSTRIAL NETWORKING EQUIPMENT USED FOR AUTONOMOUS VEHICLES

CYBERSECURITY: PROTECTING INDUSTRIAL CONTROL SYSTEMS

HOW INDUSTRIAL NETWORKING CAN PROVIDE SECURITY FROM DRONES
.webp)
Thermal Cameras Reveal How to Keep Your Home Cool During a Heat Wave

FLıR ONE PRO
.png)
Unmatched Maritime Awareness with Cooled Thermal Imaging
.png)
What Is the Right Handheld Thermal Camera for You?
.png)
Camera Resolution and Range
.png)
Special Applications for Marine Cameras
.png)
What’s The Difference between Thermal Imaging and Night Vision?
.png)
Can Thermal Imaging See Through Fog and Rain?

Which Cx-Series Camera Is Right for You?
.png)
What is MSX®?

Five Reasons Maritime First Responders Need Thermal Imaging
.png)
3 Distinguishing Features of Superior Thermal Cameras
.png)
Determine Which Visible and Thermal Security Cameras You Need

Bullet vs. PTZ vs. Dome: Which Security Camera Is Right for You?
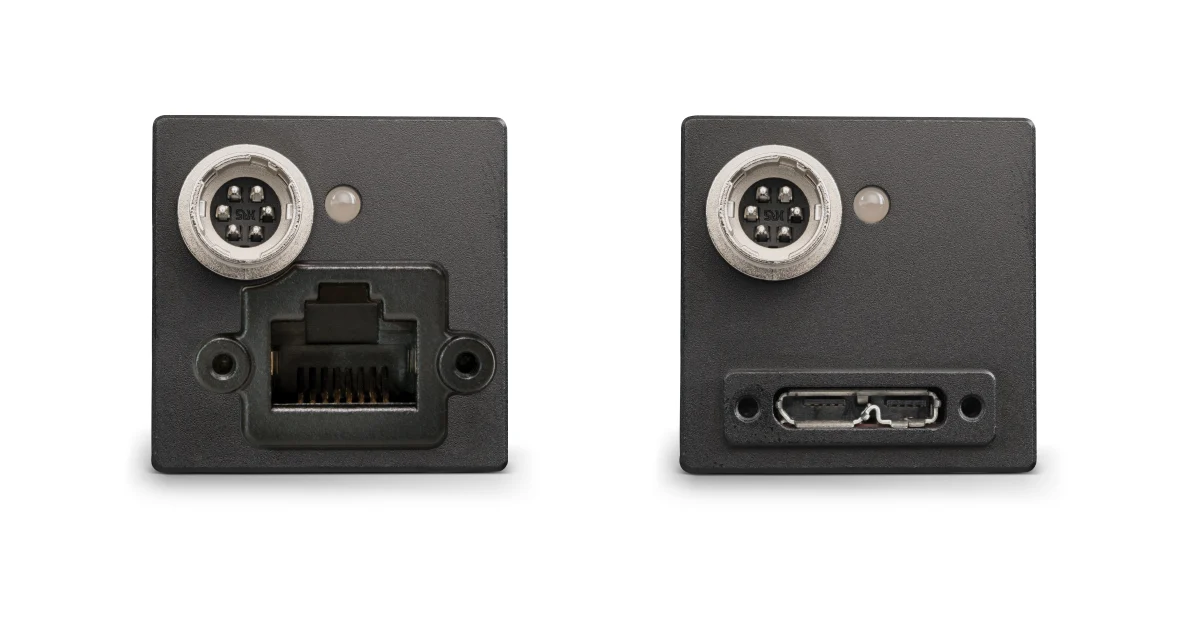
Interfaces for Machine Vision
Machine Vision Sensor Review
.png)
Teledyne FLIR, the Industry Leader, Launches Boson +, a Long-Wave Infrared Thermal Imager Module with an Accuracy of Less Than 20 mK
.png)
Whitepaper: IP-Based Security Convergence
.png)
3 Technologies Transforming Safe Cities into Smart Cities
.png)
Insights from the Field: Ensuring Workplace Safety Using Thermal Camera Screening for Entry Control

Thermal Night Vision as a Force Multiplier
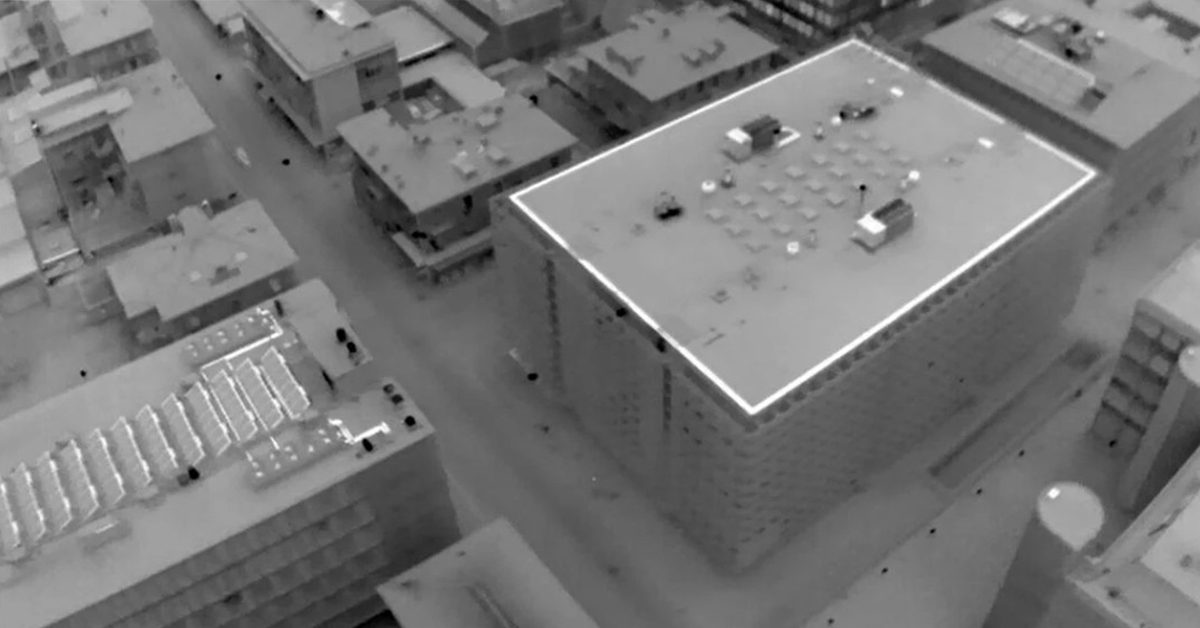

Can Thermal Imaging See Through Walls? And Other Common Questions
Application Spotlight: Early Fire Detection for Rapid Heat Generation
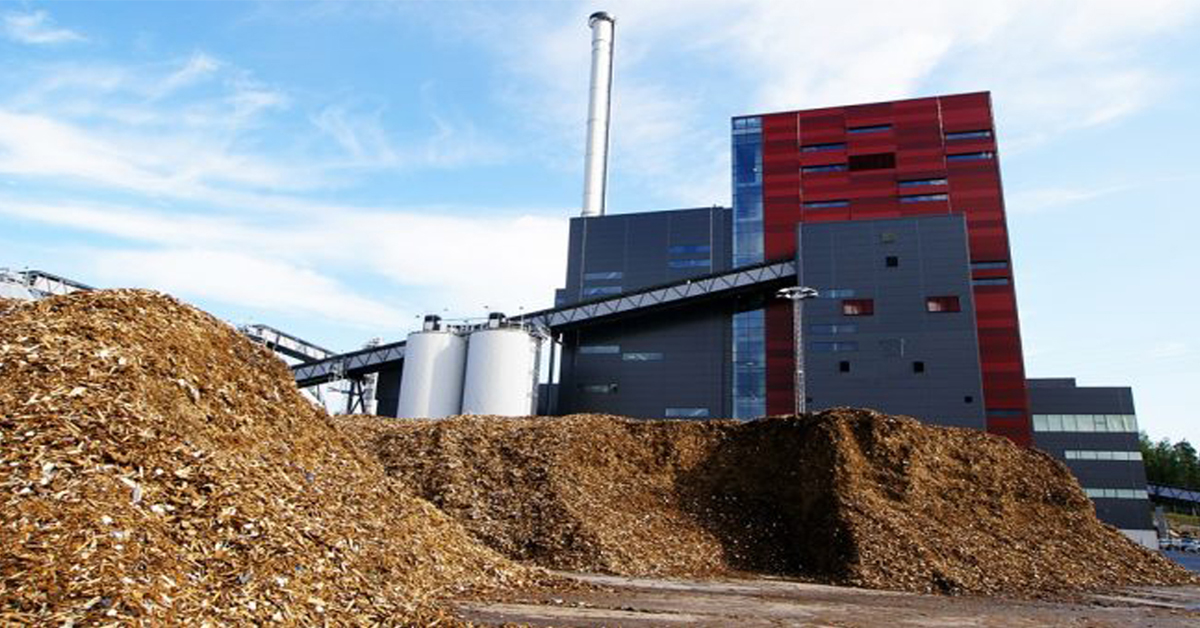

Protect Personnel and Equipment by Detecting Early Signs of Fire

Teledyne FLIR Launches A500f/A700f Cameras for Fire Detection and Condition Monitoring
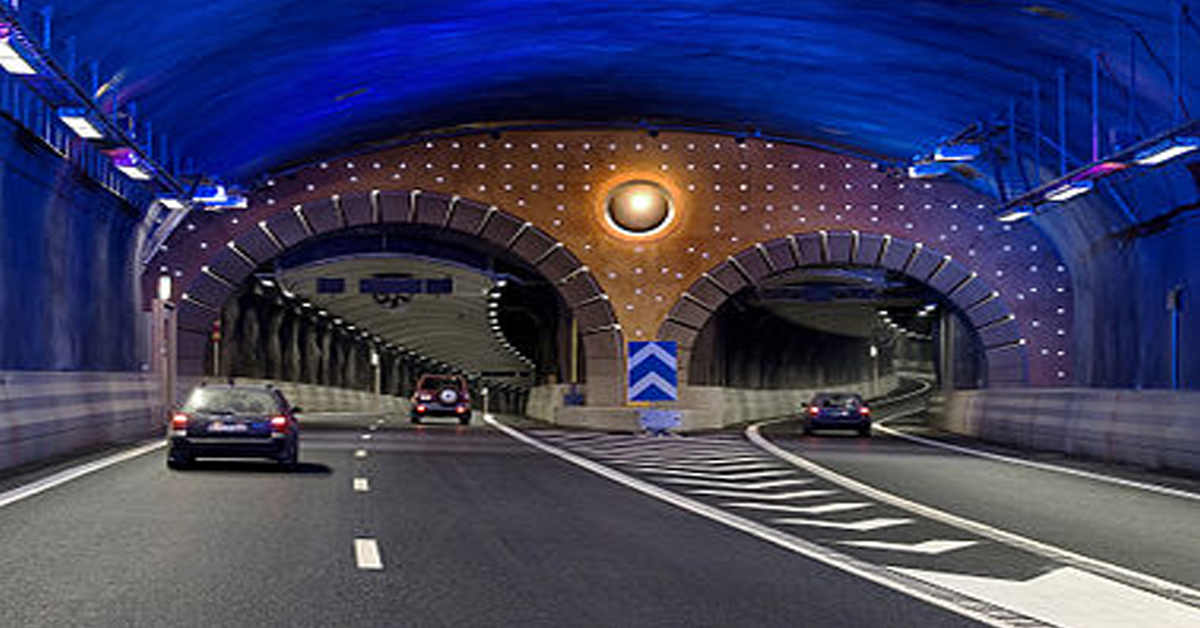

Thermal Imaging Cameras Help Guarantee Fire Safety in Tunnels

Thermal Imaging Cameras Help to Prevent Fires

ITS-Series Dual AID Surpasses Standards for Fire Detection Systems in Japan

How Layering Multispectral PTZ Cameras and Radars Improve Perimeter Protection
POWER REMOTE RESET TECHNOLOGY - PRRT

Why Yacht Owners are Adding Thermal Imaging Cameras to Minimise the Risk of Lithium-Ion Battery Fires?
.png)
Intelligent Transportation Systems

Best Practices Guide for Perimeter Security Applications

Protect Pedestrians, Bicyclists and More with Thermal Smart Sensors

White Paper: Application of Ground-Based Security Radar to Perimeter Systems

What is Thermal Leakage and How to Reduce Its Risks

Battery Inspection Using Advanced Thermography

Providing ire Protection for Lithium Battery Storage

The Power of Thermal Imaging
.png)
Why Panel PCs Are Perfect For Industrial Applications?

Teledyne DALSA
.png)
Advantages of Virtual Barrier Video Analytics for Perimeter Security Systems
.png)
.png)
NASA Takes the Teledyne FLIR Boson Thermal Camera Module Out of this World
.png)
Port Security Enhancement: DP World Yarımca's Trust in FLIR Security Solutions for Effective and Safe Port Operations
.png)
The Importance of Thermal Sensitivity (NETD) for Detection Accuracy
.png)
Bosphorus Boat Show 2025: The Meeting Point of the Maritime World

Application Spotlight: Critical Asset Monitoring for Thermal Conditions
.png)
Thermal Imaging for Marine Firefighting

Imaging in Mobile Mapping
.png)
Using Thermal Imaging for Oil Spill Detection

Five Reasons Maritime First Responders Need Thermal Imaging

Case Study: Tackling Compressed Air Leaks in Automotive Parts Manufacturing with Acoustic Imaging

Thermal Night Vision as a Force Multiplier
.png)
Line Scan Contact Image Sensor - AxCIS

Beyond Resolution: What Really Makes a Camera System Work for Mobile Mapping
.png)
Multispectral Marine Cameras for USV Applications
.png)
Stabilizing FLIR Cameras for Smooth Viewing in Rough Waters
 (1).png)