UNDERSTANDING WHAT THE INDUSTRIAL INTERNET OF THINGS IS
Introduction
Many people are aware of the internet of things; however, fewer recognize the use and potential of the industrial internet of things. Also known simply as the Industrial Internet, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is implemented in a wide range of industries and continues to grow in popularity each day. To gain a better understanding of what the industrial internet of things is, continue reading this comprehensive guide.
What is the Industrial Internet of Things?
The industrial internet of things essentially refers to the expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT) and its use in industrial applications, from robotics to medical devices. It is composed of billions of industrial devices and machines that are equipped with sensors and connected to wireless networks, which allows them to gather and share mass quantities of data. The IIoT focuses heavily on machine-to-machine communication, machine learning, and big data. In doing so, it allows industrial industries to improve the efficiency, consistency, and reliability of their operations.
How the IIoT Differs from the Internet of Things
While there is some overlap between the IIoT and the internet of things, they differ in several ways. Most obviously, the industrial internet of things contains industrial-grade devices rather than the typical consumer-level devices used in the internet of things.
Another one of the main distinctions between these two systems is their use of information technology (IT) and operational technology (OT). In the industrial internet of things, IT and OT intersect. This convergence allows industries to formulate a greater system integration. As a result, benefits such as improved automation, optimization, and decision making can all be achieved.
Advantages of the IIoT
1. More Informed Decision Making
Perhaps the most notable advantage of the IIoT is its ability to improve the decision-making process for businesses. By connecting industrial devices, advanced analytics, and people into one cohesive network, a system that can collect, monitor, exchange, analyze, and deliver valuable insights is formed. In creating and communicating such insights in real-time, the IIoT allows companies to make more informed decisions more quickly. This capability is highly beneficial in time-sensitive industries that rely on high degrees of accuracy.
2. Increased Efficiency
Through analysis of the data that comes in through the sensors in the system, businesses can find ways to make their processes more efficient. In addition to receiving insights on how to improve the efficiency of processes, the IIoT enables machines to automate more tasks. Such automation has the potential to further improve the efficiency of a company by minimizing the potential for human error which can often impede production.
3. Enhanced Scalability
The IIoT also allows businesses to enhance their scalability. In enabling businesses to collect and analyze far larger quantities of data at rapid speeds through the implementation of connected smart devices, they have the capability to expand their operations larger than ever before.
4. Reliability
Another key advantage of the industrial internet of things is its ability to greatly enhance the reliability of an operation. In acquiring valuable data regarding industry operations and the status of devices and machinery, the IIoT allows companies to identify potential issues early on and make more accurate predictions on when machines will need servicing. In doing so, the IIoT can significantly reduce downtime in a company and enhance the reliability of its operations, which is essential for the reputation, financial wellbeing, and success of any organization. This capability is especially impactful in high-stakes industries such as the healthcare field where power outages or system failures can have detrimental impacts.
Applications for the Industrial Internet of Things
The industrial internet of things is an increasingly popular construct that is used in a wide range of applications. Due to its ability to increase efficiency and improve decision making, the industrial internet of things is often implemented in industries where consistent, reliable operation is vital. For example, healthcare, power generation, oil and gas industries, and other high-stakes fields often implement the industrial internet of things to avoid downtime that can be potentially life-threatening or otherwise detrimental to their operations.
That being said, the industrial internet of things isn’t only implemented in particularly high-stakes applications. The IIoT is also often used in retail industries to identify and eliminate supply chain bottlenecks or in the manufacturing industry to decrease downtime by providing manufacturers with a comprehensive view of production line operation and the status of machines. The IIoT is also useful in transportation industries to monitor the performance of their vehicle fleets or in utility industries to monitor remote locations and operations.
While the IIoT is most commonly adopted by larger corporations, it will likely become more widely implemented by smaller organizations as the cost of services and hardware steadily decreases. In other words, the potential for the expansion and implementation of the IIoT is virtually limitless.
Challenges and Risks of Implementing the IIoT
While the IIoT offers numerous advantages and is successfully implemented in a wide range of industries, adopting this system is not without its challenges and risks. Some of the key challenges of the industrial internet of things include:
- Maintaining Security: Increasing connectivity while maintaining security is one of the most significant challenges and risks of implementing the industrial internet of things. If a hacker gains access to a connected system, the entire system may be subject to a major breach and operations could potentially be entirely shut down. As such, industries that seek to adopt the IIoT must take the necessary measures to manage the physical and digital components in their network securely.
- Integration: Many corporations still use legacy systems and processes that have remained unaltered for decades. As such, adopting new technologies and integrating them with legacy systems can pose a significant challenge.
- Fragmentation: Fragmentation has been a top concern when adopting IoT technology. Concurrently, creating a system in which differing standards, protocols, and architectures all work together seamlessly also poses a challenge when implementing IIoT systems.
Now that you have a good understanding of what the industrial internet of things is, we can step in and fulfill your IIoT needs. Antaira Technologies is an industry-leading developer and manufacturer of high-quality industrial networking and communication products. For over a decade, we have offered an extensive range of innovative industrial networking products suitable for use in even the most rugged environments. From industrial routers to industrial Ethernet switches, you can find everything you need to create a reliable, durable network. For more information regarding our products, contact us today.
Blog Posts

Thermal Camera Selection
How Far Can I See?
How Should Human Temperature Be Measured?
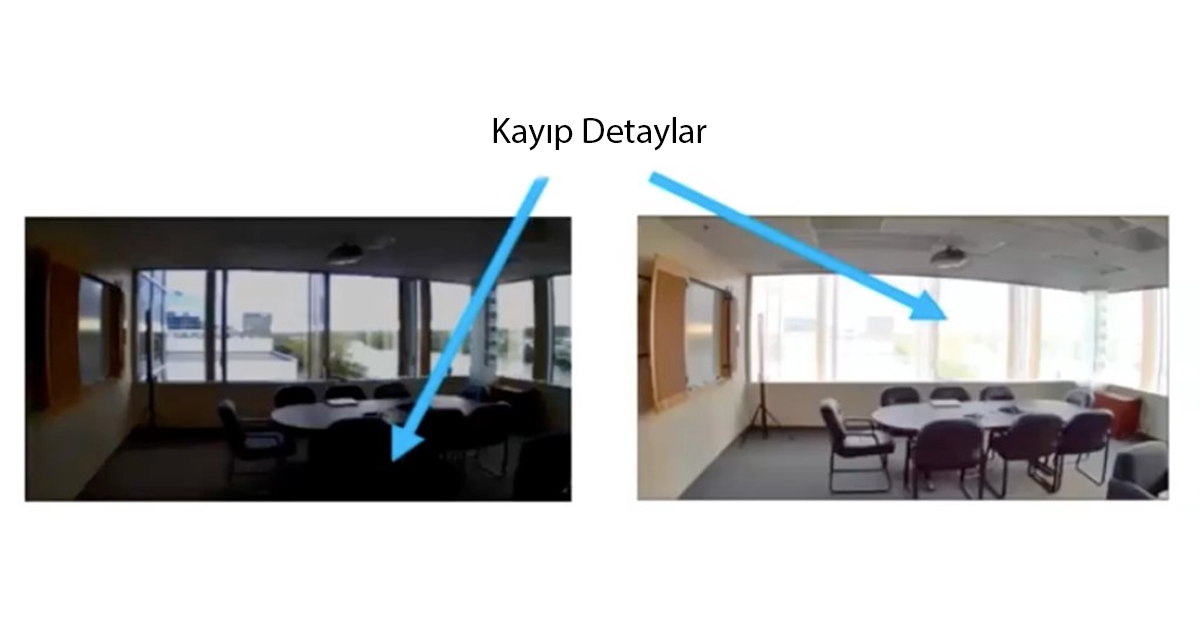

What is Wide Dynamic Range?

MYNOISE AUDIO MIXER REVIEW

WHAT IS A WIRELESS DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM?

POE VS. POE+ VS. POE++: CHOOSING THE RIGHT INDUSTRIAL ETHERNET SWITCH FOR YOU

INDUSTRY-LEADING INDUSTRIAL ETHERNET SWITCHES
UNDERSTANDING WHAT THE INDUSTRIAL INTERNET OF THINGS IS
THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN A HUB, SWITCH, & ROUTER

5 Benefits of Thermal Imaging Cameras

DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INDUSTRIAL ETHERNET AND REGULAR ETHERNET

INDUSTRIAL NETWORKING EQUIPMENT USED FOR AUTONOMOUS VEHICLES

CYBERSECURITY: PROTECTING INDUSTRIAL CONTROL SYSTEMS

HOW INDUSTRIAL NETWORKING CAN PROVIDE SECURITY FROM DRONES
.webp)
Thermal Cameras Reveal How to Keep Your Home Cool During a Heat Wave

FLıR ONE PRO
.png)
Unmatched Maritime Awareness with Cooled Thermal Imaging
.png)
What Is the Right Handheld Thermal Camera for You?
.png)
Camera Resolution and Range
.png)
Special Applications for Marine Cameras
.png)
What’s The Difference between Thermal Imaging and Night Vision?
.png)
Can Thermal Imaging See Through Fog and Rain?

Which Cx-Series Camera Is Right for You?
.png)
What is MSX®?

Five Reasons Maritime First Responders Need Thermal Imaging
.png)
3 Distinguishing Features of Superior Thermal Cameras
.png)
Determine Which Visible and Thermal Security Cameras You Need

Bullet vs. PTZ vs. Dome: Which Security Camera Is Right for You?
Interfaces for Machine Vision
Machine Vision Sensor Review
.png)
Teledyne FLIR, the Industry Leader, Launches Boson +, a Long-Wave Infrared Thermal Imager Module with an Accuracy of Less Than 20 mK
.png)
Whitepaper: IP-Based Security Convergence
.png)
3 Technologies Transforming Safe Cities into Smart Cities
.png)
Insights from the Field: Ensuring Workplace Safety Using Thermal Camera Screening for Entry Control

Thermal Night Vision as a Force Multiplier

Can Thermal Imaging See Through Walls? And Other Common Questions
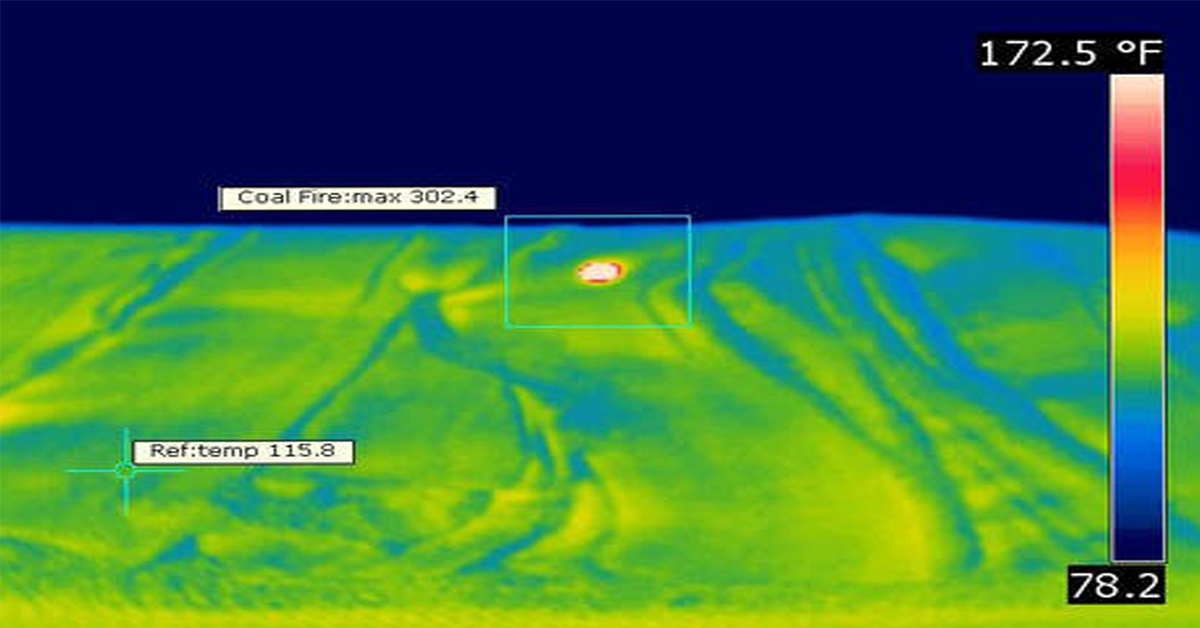
Application Spotlight: Early Fire Detection for Rapid Heat Generation

Protect Personnel and Equipment by Detecting Early Signs of Fire

Teledyne FLIR Launches A500f/A700f Cameras for Fire Detection and Condition Monitoring

Thermal Imaging Cameras Help Guarantee Fire Safety in Tunnels

Thermal Imaging Cameras Help to Prevent Fires

ITS-Series Dual AID Surpasses Standards for Fire Detection Systems in Japan

How Layering Multispectral PTZ Cameras and Radars Improve Perimeter Protection
POWER REMOTE RESET TECHNOLOGY - PRRT

Why Yacht Owners are Adding Thermal Imaging Cameras to Minimise the Risk of Lithium-Ion Battery Fires?
.png)
Intelligent Transportation Systems

Best Practices Guide for Perimeter Security Applications

Protect Pedestrians, Bicyclists and More with Thermal Smart Sensors

White Paper: Application of Ground-Based Security Radar to Perimeter Systems

What is Thermal Leakage and How to Reduce Its Risks

Battery Inspection Using Advanced Thermography

Providing ire Protection for Lithium Battery Storage

The Power of Thermal Imaging
.png)
Why Panel PCs Are Perfect For Industrial Applications?

Teledyne DALSA
.png)
Advantages of Virtual Barrier Video Analytics for Perimeter Security Systems
.png)
.png)
NASA Takes the Teledyne FLIR Boson Thermal Camera Module Out of this World
.png)
Port Security Enhancement: DP World Yarımca's Trust in FLIR Security Solutions for Effective and Safe Port Operations
.png)
The Importance of Thermal Sensitivity (NETD) for Detection Accuracy
.png)
Bosphorus Boat Show 2025: The Meeting Point of the Maritime World

Application Spotlight: Critical Asset Monitoring for Thermal Conditions
.png)
Thermal Imaging for Marine Firefighting

Imaging in Mobile Mapping
.png)
Using Thermal Imaging for Oil Spill Detection

Five Reasons Maritime First Responders Need Thermal Imaging

Case Study: Tackling Compressed Air Leaks in Automotive Parts Manufacturing with Acoustic Imaging

Thermal Night Vision as a Force Multiplier
.png)
Line Scan Contact Image Sensor - AxCIS

Beyond Resolution: What Really Makes a Camera System Work for Mobile Mapping
.png)
Multispectral Marine Cameras for USV Applications
.png)
Stabilizing FLIR Cameras for Smooth Viewing in Rough Waters
 (1).png)